Navigating a file system
Open your terminal or git BASH (if you are using a Windows machine).
Note: ensure you are using git BASH and not the Windows command prompt, some of these commands will differ and we’re aiming for consistent ways of working across many operating systems.
git Bash
As mentioned in the intro to unix and gitbash, git BASH is a BASH emulator, we use this to interact with the Windows OS using a UNIX-like shell with Bash commands.
Commands and flags
You can use commands to interact with the file system, for example to change directory, copy files and many other useful tasks.
When using a command they often have optional parameters called flags. These flags pass additional context and information, one common example is --help which provides information on the application you’re using.
Common shell commands:
Where am I?
Find out where you are using:
pwd

The result returned tells me I’m in the directory /Users/adamdewberry
List files and folders
List directory contents.
Useful flags:
-llist view-ashow hidden (dot) files and folders
Invocation:
ls -al
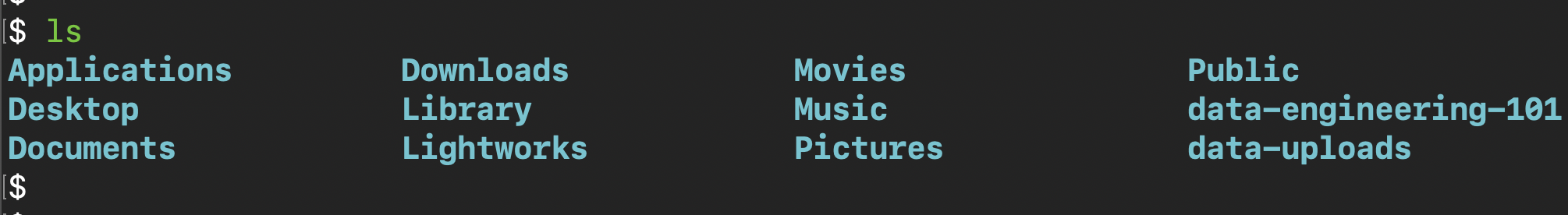
Make a new directory
Invocation:
mkdir data-engineering-101

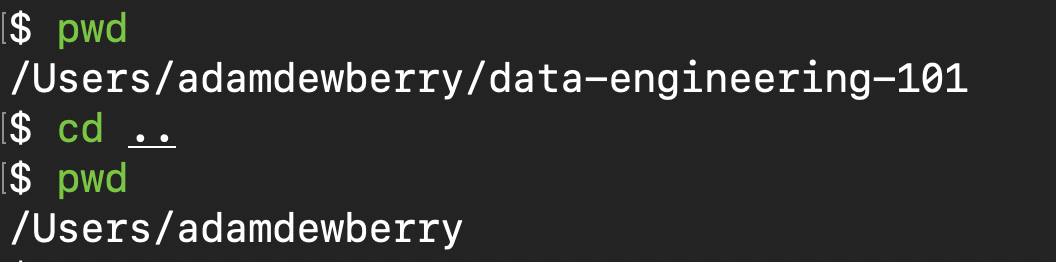
Change directory
Invocation:
cd data-engineering-101

To go back a level in your directory tree:
cd ..
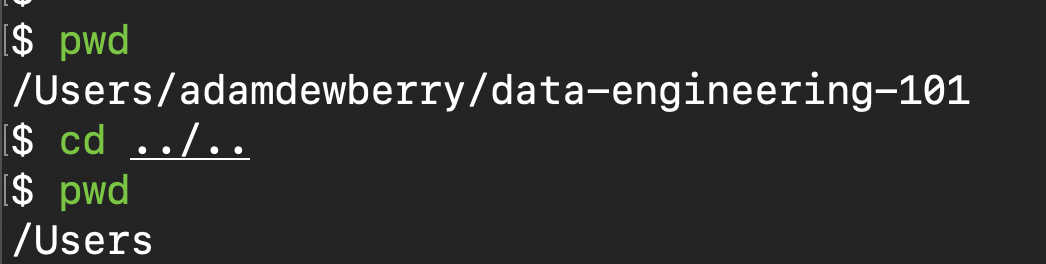
Two levels
cd ../..
Printing to the terminal
Invocation:
echo "Print a string of text to the terminal"

Sending shell output to a file
In other words, creating a file and inserting the output from your command.
Invocation:
echo "Print a string of text to the terminal" >> file.txt

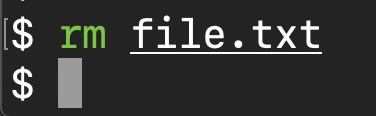
Remove files or directories
To delete a file or directory use the remove command.
Invocation:
rm file.txt
To remove a directory and its contents you will need the flag -r which stands for recursive, to remove the files recursively (the directory and everything in it):
mkdir dir-name/
rm -r dir-name/